|
Customer Counter & Video Analytics |
 |
A people counter is a device that can be used to measure the number and direction of people traversing a certain passage or entrance. |
|
Use cases |
|
Retail stores |
 |
Conversion Rate: People counting systems in the retail environment are used to calculate the conversion rate, i.e. the percentage of visitors that make purchases. This is a key indicator of a store's performance and may provide more valuable information than traditional methods, which only take into account sales data. Taken together, traffic counts and conversion rates can reveal important sales information, such as why a specific store is experiencing more sales, whether or not year-over-year sales are down, why fewer people are visiting a store, or why fewer people are making purchases. Marketing Effectiveness: Shopping mall marketing professionals rely on visitor statistics to measure their marketing. Often, shopping mall owners measure marketing effectiveness with sales, also utilizing visitor statistics to scientifically measure marketing effectiveness. Marketing metrics such as CPM (Cost Per Thousand) and SSF (Shoppers per Square Foot) are performance indicators that shopping mall owners monitor to determine rent, according to the total number of visitors to the mall or according to the number of visitors to each individual store in the mall. Staff Planning: Accurate visitor counting is also useful for optimizing staff shifts. Staff requirements are often directly related to the density of visitor traffic, and services such as cleaning and maintenance are typically undertaken when traffic is at its lowest. |
 |
|
Monitoring of High-Traffic Areas: Shopping centers use people counters to measure the number of visitors. People counters also assist in measuring the areas of 'hot spots', where statistics gathered by people counters are often used to justify rental rates. |
|
Museums and libraries |
 |
Funding Justification: Many non profit organizations use visitor counts as evidence when making applications for finance, for use when planning for seasonal staffing, and other strategic operational decisions. In cases where tickets are not sold, such as in museums and libraries, counting is either automated, or staff keep a log of how many clients use different services. |
|
Stadiums and Concert Halls |
 |
Crowd Management: There are often large traffic flows before and after an event. People counters are used to measure the traffic flows of previous events, and the traffic patterns are used to improve traffic flow, particularly when entering and exiting. |
|
Smart Office buildings |
Energy Usage Optimization: Commercial buildings utilize people counters to measure the use of different parts of the building at different times. This information can then be used to intelligently optimize the energy usage in the building (e.g. air conditioning needs, etc.).
Fire Management: In the case of fire, people counters are one of the tools used to approximate the number of people inside the building.
|
Business Metrics |
Footfall
Footfall measures the number of people entering and exiting a venue.
Window Conversion Rate
Window Conversion Rate is the percentage of shoppers who enter a store over in relation to the number of people who walk by it. With Wi-Fi counting, shops can estimate the number of people who walk past a store. A more accurate method is video counting. While revenue and footfall are important, the number of people who walk past a store often reflects the true potential of the store location. The Window Conversion Rate often depends on the attractiveness of the shop window design and the effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
Visit Duration
Visit duration is the amount of time visitors stay in a venue. WiFi counting has the ability to track both the time a person carrying a smartphone has entered the venue and when that same person has left the venue.
Returning Customers
This metric looks at the number of people entering a store who had visited the store previously. WiFi counting has the ability to remember the Unique WiFi beacon signal ID emitted by shoppers, so if a shopper has previously visited a store, the counter flags the person as a returning customer.
Cross-Shopping
This is the number of shoppers who enter a store who have previously visited other stores of the same chain. This is available for third-generation people counters that have WiFi counting functionalities.
|
Technologies |
Many different technologies are used in people counting devices, such as infrared beams, thermal imaging, computer vision, and WiFi counting.
1st Generation: Infrared Beam Counters
 |
The simplest form of counter in which a single, horizontal infrared beam across an entrance counts when a person or object passes and breaks its beam The simplest form of counter is a single, horizontal infrared beam across an entrance which is typically linked to a small LCD display unit at the side of the doorway. Such a beam counts a 'tick' when the beam is broken, therefore it is normal to divide the 'ticks' by two to get visitor numbers. Beam counters usually require a receiver or a reflector mounted opposite the unit with a typical range from 2.5 metres (8ft 2 in) to 6 metres (20ft). Despite its limitations, infrared counters are still widely used, primarily due to their low cost and simplicity of installation. |
2nd Generation: Thermal counter.
Thermal imagine systems use array sensors that detect heat sources. These systems are typically implemented using embedded technology and are mounted overhead for high accuracy.
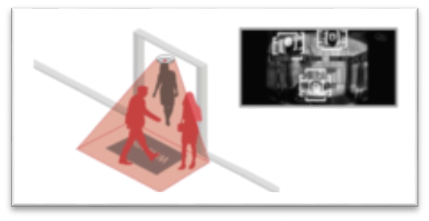 |
Thermal imaging systems use array sensors which detect heat sources from human body.
Before the advance of computer technology that allows complex algorithms to perform video counting, thermal counters were the main choice for most businesses. They are fairly accurate; however they do have their limitations: |
i) Thermal counters cannot be mounted on a high ceiling;
ii) Can only cover a narrow door entrance;
iii) Difficult to verify the accuracy of the counter;
iv) Accuracy is reduced in places with slight variations in thermal conditions.
3rd Generation: Video & WiFi counting
With the advance of computer technology, complex image processing algorithms can now be used to perform counting using camera imaging. The third generation counters also include Wifi Counting functionality, which collects WiFi probe request signals from shoppers' smartphones and adds a number of important metrics for businesses, especially for the retail industry.Many business are now deploying people counters to help them to gain insight into their clients.
Video Counting
 |
WiFi Counting |
WiFi Counting uses a WiFi receiver to pick up unique WiFi management frames emitted from smartphones with a range of up to 100 meters. While not all people carry a smartphone, WiFi counting can produce statistically significant metrics due to the large sample size available. Apple iOS8 attempts to randomise MAC address, however it makes little impact on the effectiveness of WiFi counting.Apple iOS9 and Android 6.0 Marshmallow use more aggressive MAC rotation schemes, making WiFi counting impractical in the future.
|
What are Video Anaytics? |
Video analytics software was created to help review the growing hours of surveillance video that a security guard or system manager may never have time to watch - your video surveillance system is only as useful as the incidents you can actually capture and watch, and video analytics will help you find them.
Using video analytics makes your surveillance system more efficient, reduces the workload on security and management staff, and helps you capture the full value of security video by making your IP camera system more intelligent in its work.
How Video Analytics Software Works
Video analytics software for security cameras is available in several forms: installed on your camera, on your NVR, or as 3rd party software you buy. Each version will do the same thing, however - monitor your videos to search for and alert you to activity.
Each video analytics solution will work a bit differently depending on the manufacturer and application. They all work in the same basic way, however - when setting up the software you set up parameters to the activity the software is looking for, set up the alert notification system, and when the software detects something that meets its search criteria it alerts you.
For example, many businesses use surveillance systems to detect motion in their store after hours. You can set your system to motion detection during the hours your business is closed, so if it detects motion it will send you an email - a quick response that may help you react quickly to a break-in or accident.
How Video Analytics Can Help You
The old idea of a video surveillance system is of a security guard sitting in a booth watching the security camera feed live, hoping to catch suspicious activity. This model relies on having a live person watching and reviewing all your video, however, which is not practical or efficient. Different security guards may have differing levels of focus or different ideas of suspicious activity.
Video management software changes this system by using software to monitor your video feed around the clock, alerting you to activity so you only need to watch the cameras when something happens. This will help you best utilize your surveillance system, saving you time and effort.
Video analytics can be used for:
- Motion detection
- Facial recognition & license plate reading
- People counting & dwell time monitoring for retail stores
- Recognizing long lines at checkout and sending alerts
- And more - Contact our video surveillance experts today to get personalized recommendations for your needs!
Video analytics software comes with a wide range of features, making them easy to fit into any surveillance system. Choose from software that supports every system, from the smallest systems to large multi-campus systems. A variety of leading manufacturers create video analytics software, including Surveon.
Analytics uses mathematical algorithms to monitor, analyse and manage large volumes of video. It digitally analyses video inputs; transforming them into intelligent data which help in taking decisions.
Video Analytics can be real-time – configured to track and provide alerts to specific incidents as they happen – or post event – retrospectively searching for incidents that have already occurred.
Video Analytics Architecture
Video analytics applications can run at the centre (on servers or DVRs at the central monitoring station), at the ‘edge’ (built into cameras) or as a combination of both.
The ‘edge’ solutions are ideal to locate live analytics. Central real-time processing can run out of steam based on the no. of cameras in the network, processing power and the network bandwidth; whereas in the ‘edge’ solution, every camera has dedicated processing. Customers with limited bandwidth on their networks can opt for an analytics solution at the ‘edge’, so that only information on suspicious incidents gets sent through the network; and hence, doesn’t use up network bandwidth.
The optimal place to locate post-processing analytics is obviously on a central server, so that recorded video can be searched many times, with different parameters. Using analytics a user can search large amounts of recorded video for possible events and then verify the results. End user companies with existing infrastructure, who want to upgrade by adding analytics to some of their existing cameras, may find integrating analytics to the central server a cost-effective and flexible solution.
Applications
Video surveillance analytics are finding numerous applications in both the public and private sectors; in government, retail, transport and financial services. These applications protect people and assets against harm and damage, ideally before events occur. Systems enabled with video analytics work on two key concepts: motion detection and pattern recognition.
Motion Detection: By examining each pixel in the frame, the video analytics software is able to pick up even the slightest movement.
Pattern Recognition: Video analytics help distinguish objects within a video frame. Specific patterns/objects can be programmed, which will be recognized within the frame. Should any change happen, i.e. object is moved, goes missing, or new object added; the software immediately recognizes it and sends out an alert.
Typical applications of Video Analytics in security and surveillance include:
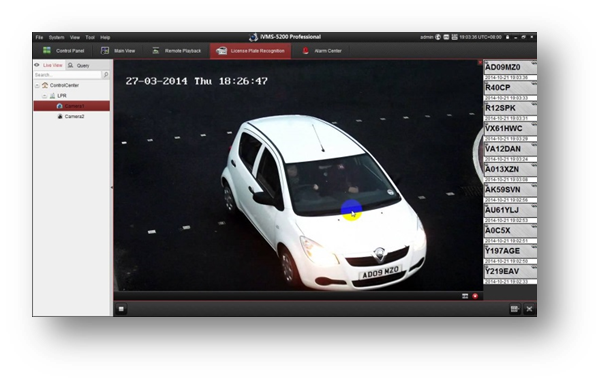
> License Plate Recognition
> Security Access Point Monitoring
> Perimeter Protection / Intrusion Detection
> Abandoned Object
> Object Removal
> Camera Tampering
Video analytics is also gaining popularity in the retail segment for market analysis. A lot of the analytics information can be valuable for marketing teams in companies. These include:
> Footfalls (People counting)
> Gender counting
> Display/shelf space effectiveness and
> Forensics analysis of data to determine trends
Benefits of Video Analytics
Controlling and managing a video surveillance system is difficult; especially if you are working with a large number of cameras. Keeping track of everything that is going on is a hassle and requires a lot of manpower.
This is not the case with video analytics. Video analytics use detailed and sophisticated algorithms to examine digital video feeds. Video images are examined pixel by pixel, missing absolutely nothing. Analytics filters can be intelligently tailored to meet specific security or business needs.
Some of the filters/algorithms that help in the above are:
> Direction filters with independent adjustment of acceptable direction and angle
> Dwell filter with variable time threshold.
> Speed filter with upper and lower speed thresholds
> Object filters to filter out birds, small animals, blowing trash and other such clutter
Limitations of Video Analytics
 |
While video analytics holds great promise, the jury is still out on the efficacy of the technology in the real world. The key thing to note here is that video analytics technology is still in its infancy.
Current video analytics solutions do work, but in a constrained environment. For example, video analytics if used for perimeter security or vehicle license plate recognition or unattended baggage in a public space, will work; provided weather conditions are not extreme, the number of vehicles is not very high, or in an not so crowed location, respectively. On the other hand, if a user wishes to identify unattended baggage in a busy railway station at peak hours, he will surely be disappointed; as the system will end up generating too many false alerts. Thus, keep in mind that the success of a video analytics implementation will be determined by the use it is put to and in situ conditions. |
|
Overview |
How a CCTV People Counting System Works
Tests show video people counting achieves over 98% accuracy. This is how it's done.
-
Overhead closed-circuit television (CCTV) camera tracks people's movements.
-
The camera connects to a people counter which accurately detects and records how many people pass through the counting zone.
-
The people counters stream video and data to a central PC over Wi-Fi, Internet, IP, Ethernet, RS485 or RS232.
-
Counts can be combined with live sales data in a POS database, giving real-time sales conversion figures.
-
Wide entrances and areas are handled by linking several cameras across the ceiling.
-
People are counted as they cross through a zone of the picture and exit up, down, left or right depending on your settings.
-
The embedded video server lets you view live video footage alongside the people counts, so you can accurately verify, and configure, the system over the internet from anywhere in the world.
-
Once set up, counts alone can be sent over the network to save bandwidth.
-
Replay counting videos for off-site commissioning
-
Choose the time period over which counts are measured: every hour or every 5 minutes for example.
-
Change settings in software to optimise the count accuracy, for each door if necessary, for example
-
Deal with shadows and poor light
-
Set for crowd counting
-
Increase the sensitivity of the people detection
-
Adjust for indoors and outdoors
Video Analytics
Video analytics means the computerised analysis of video streams, particularly from CCTV cameras. A Video Turnstile counting unit connects to a CCTV camera and performs real-time analysis of the video for immediate detection and counting of people. During setup, video and analysis can be streamed to a central PC where the settings and counts can be seen—as in the video above.
Our image processing algorithms are over 98% effective at identifying people entering and leaving counting zones.
The Video Turnstile people counters are independent of the video cameras.
There are two types of Video Turnstile unit: one that counts people which is called a VT, and one that saves the counts, which is called a Logger. Each counting system needs at least one Logger. The Logger can save counts from up to 16 VTs. Each camera connects to a VT. The system is thus infinitely scaleable. If you need more counting areas just add more cameras and VTs. At regular intervals the Loggers transmit their counts to the central computer.